Dive into the world of credit score ranges explained, where numbers hold the key to financial opportunities and pitfalls. Discover how these ranges impact your financial decisions and what factors play a crucial role in determining where you stand.
Explore the different credit score ranges used by major credit bureaus and how they can affect your creditworthiness in the eyes of lenders.
Understanding Credit Score Ranges
Credit score ranges are numerical representations of an individual’s creditworthiness. These ranges help lenders evaluate the risk of lending money to a particular borrower. The higher the credit score, the more likely a borrower is to repay debts on time.
Typical Credit Score Ranges
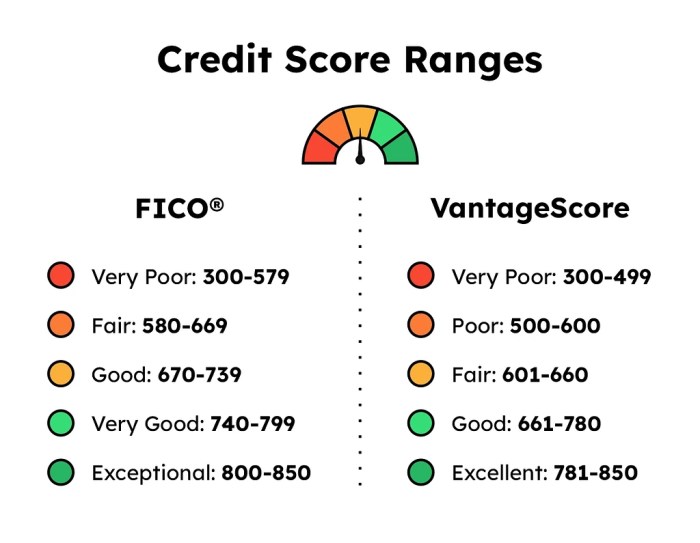
- FICO Score: The most commonly used credit score range is the FICO Score, which ranges from 300 to 850. A score above 670 is considered good, while a score above 800 is excellent.
- VantageScore: Another popular credit score range is the VantageScore, which also ranges from 300 to 850. A score above 700 is generally considered good, while a score above 750 is excellent.
Significance of Credit Score Ranges
- Credit score ranges play a crucial role in financial decision-making, influencing the interest rates on loans and credit cards that individuals qualify for.
- Higher credit scores often result in lower interest rates, saving borrowers money over the life of a loan.
- Additionally, credit score ranges can impact an individual’s ability to secure housing, obtain insurance, or even land a job.
Factors Impacting Credit Scores
When it comes to credit scores, there are several key factors that can influence whether your score goes up or down. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining a healthy credit profile.
Payment History
Your payment history is one of the most important factors that impact your credit score. Making on-time payments consistently can have a positive impact on your score, while missing payments or making late payments can lower your score significantly.
Credit Utilization
Credit utilization refers to the amount of credit you are using compared to the total amount of credit available to you. Keeping your credit utilization low, ideally below 30%, can help improve your credit score. Maxing out your credit cards or carrying high balances can negatively impact your score.
Length of Credit History
The length of your credit history also plays a role in determining your credit score. Generally, the longer you have had credit accounts open and in good standing, the better it is for your score. Closing old accounts or not using your credit at all can have a negative impact on your score.
Types of Credit Used
Having a mix of different types of credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can positively impact your credit score. Lenders like to see that you can manage different types of credit responsibly. However, too many new accounts opened in a short period of time can signal risk to lenders and lower your score.
New Credit Inquiries
Every time you apply for new credit, a hard inquiry is placed on your credit report. Too many hard inquiries in a short period of time can lower your credit score. It’s important to be mindful of how often you apply for new credit to avoid negative impacts on your score.
Interpretation of Credit Score Ranges
Credit score ranges provide a clear indication of an individual’s creditworthiness and financial responsibility. Lenders use these ranges to assess the risk associated with lending money to a particular individual. Understanding what each range signifies is crucial in managing and improving one’s credit score.
Credit Score Ranges
- A credit score below 580 is considered poor. Individuals in this range may have a history of missed payments, defaults, or bankruptcies. Lenders may view them as high-risk borrowers.
- A credit score between 580 and 669 is fair. While not the worst, individuals in this range may still struggle to qualify for loans or credit cards with favorable terms.
- Individuals with credit scores ranging from 670 to 739 are considered good. They are more likely to qualify for loans and credit cards at competitive interest rates.
- Excellent credit scores fall in the range of 740 to 850. Individuals in this range are viewed as low-risk borrowers and can access the best loan offers with the lowest interest rates.
Lender’s Perspective
- Lenders typically prefer borrowers with higher credit scores as they are perceived to be less likely to default on their payments. Individuals with excellent credit scores are more likely to be approved for loans and credit cards with lower interest rates.
- For borrowers with poor or fair credit scores, lenders may require additional collateral or charge higher interest rates to offset the perceived risk of lending to them.
Impact on Interest Rates
- Credit score ranges directly impact the interest rates individuals are offered on loans and credit cards. Borrowers with higher credit scores are eligible for lower interest rates, resulting in lower overall borrowing costs.
- Conversely, individuals with lower credit scores may face higher interest rates, making borrowing more expensive over time. It is essential to improve credit scores to access better loan terms and save money on interest.
Improving Credit Scores
Improving your credit score is essential for better financial opportunities. By taking strategic steps, individuals can enhance their credit scores over time, leading to increased access to loans, credit cards, and other financial products.
Strategies for Improving Credit Scores
Implementing the following strategies can help individuals improve their credit scores within different ranges:
- Pay bills on time: Timely payments demonstrate financial responsibility and can positively impact credit scores.
- Reduce credit card balances: Lowering credit card balances can lower credit utilization ratios, improving credit scores.
- Regularly check credit reports: Monitoring credit reports for errors and discrepancies can help maintain accurate credit information.
- Limit new credit applications: Opening multiple new accounts can lower the average age of accounts and negatively affect credit scores.
Timeline and Effectiveness of Actions
Improving credit scores is a gradual process that can take several months to see significant changes. Consistently implementing positive credit habits can lead to long-term improvements in credit scores.
Remember, improving credit scores is a marathon, not a sprint.
Real-life Examples of Credit Score Improvement
For example, Sarah was able to increase her credit score from 620 to 750 within a year by paying off existing debts, maintaining low credit card balances, and disputing inaccuracies on her credit report. Her dedication to improving her credit habits led to a significant boost in her credit score.
