Buckle up as we dive into the fascinating world of Understanding market cycles, where trends, patterns, and economic forces collide to shape the financial landscape. Get ready for a wild ride filled with insights and revelations that will change the way you view the market forever.
From defining market cycles to exploring historical examples, this topic is a goldmine of information waiting to be uncovered.
Introduction to Market Cycles
Market cycles are the recurring patterns or sequences of economic expansion and contraction that affect the overall performance of financial markets. These cycles are characterized by different stages, each with its unique characteristics and impact on various sectors of the economy.
Stages of Market Cycles
- The Expansion Phase: During this phase, the economy experiences growth, rising employment rates, and increasing consumer spending. Stock prices tend to rise, and businesses expand their operations.
- The Peak Phase: This phase marks the peak of economic activity, with high levels of employment and consumer spending. Stock prices reach their highest point, but signs of a slowdown begin to emerge.
- The Contraction Phase: In this phase, economic growth slows down, leading to reduced consumer spending and declining stock prices. Businesses may start cutting back on investments and laying off employees.
- The Trough Phase: The trough phase is the lowest point of the cycle, characterized by high unemployment rates and low consumer confidence. Stock prices hit bottom, but this phase sets the stage for the next expansion.
Examples of Historical Market Cycles
- The Dot-Com Bubble (1995-2000): The rapid growth of internet-based companies led to a speculative bubble that burst in the early 2000s, causing a significant market downturn.
- The Great Recession (2007-2009): The collapse of the housing market and financial institutions triggered a global economic crisis, resulting in a severe recession and stock market crash.
Factors Influencing Market Cycles
Understanding the factors that influence market cycles is crucial for investors looking to navigate the ups and downs of the financial markets.
Economic Indicators Impacting Market Cycles
- GDP Growth: A strong GDP growth usually signals a healthy economy, leading to positive market cycles.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment rates can indicate a struggling economy, negatively impacting market cycles.
- Inflation Rates: High inflation rates can erode purchasing power, affecting market cycles.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates by central banks can influence borrowing costs and investment decisions, impacting market cycles.
Investor Sentiment and Market Cycles
- Investor Confidence: Positive investor sentiment can drive market cycles upwards, while fear and uncertainty can lead to downturns.
- Herd Mentality: The tendency of investors to follow the crowd can amplify market cycles, leading to bubbles and crashes.
- Risk Appetite: Investor risk appetite can influence market cycles, with higher risk tolerance leading to more aggressive market behavior.
Government Policies and Market Cycles
- Monetary Policy: Central banks’ decisions on interest rates and money supply can have a significant impact on market cycles.
- Fiscal Policy: Government spending and taxation policies can influence economic growth and market cycles.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations can affect market behavior and investor confidence, impacting market cycles.
Understanding Market Phases
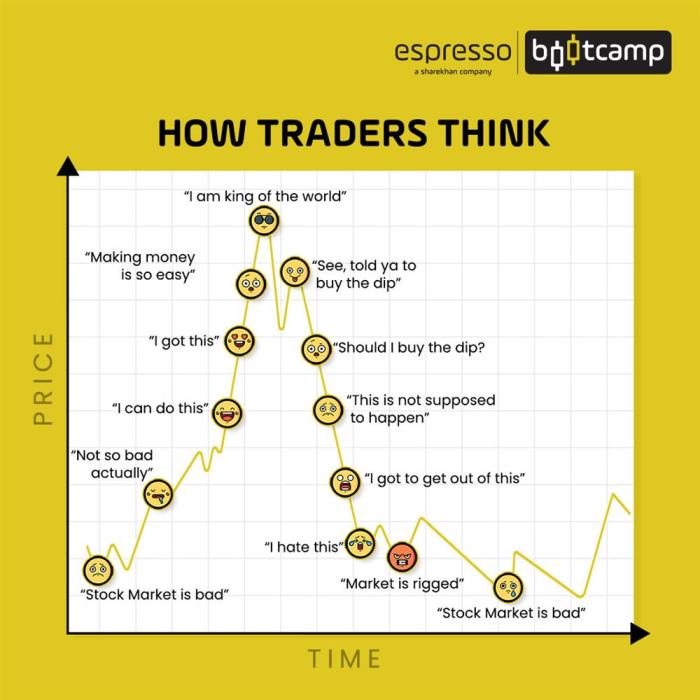
In the world of market cycles, understanding the different phases is crucial for making informed decisions and maximizing opportunities for success.
Accumulation Phase
During the accumulation phase, prices are typically at their lowest as smart money begins to enter the market. Investors who recognize the potential for growth start buying assets, slowly driving prices up. This phase is characterized by low volatility and a lack of widespread interest from the general public.
Uptrend Phase
The uptrend phase follows the accumulation phase and is marked by a significant increase in asset prices. This phase is fueled by increasing demand from both institutional and retail investors, leading to a steady rise in prices. Positive news and strong market sentiment often accompany this phase, creating an optimistic outlook among market participants.
Distribution Phase
As prices reach peak levels during the uptrend phase, the distribution phase begins. This phase is characterized by smart money and early investors starting to sell off their positions, causing prices to plateau or even decline. Market participants who entered late in the cycle may still be buying, unaware of the impending shift. This phase is crucial as it signals the end of the uptrend and the beginning of a potential downtrend.
Technical Analysis in Market Cycle Understanding
In understanding market cycles, technical analysis plays a crucial role in helping investors identify patterns and trends that can indicate where the market is heading. By using various tools and indicators, traders can make informed decisions based on historical price movements.
Moving Averages in Market Cycle Analysis
One of the key technical analysis tools used to analyze market cycles is moving averages. Moving averages help smooth out price data to identify trends over a specific period. By looking at the relationship between short-term and long-term moving averages, traders can determine whether the market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or consolidation phase.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculated by adding up the closing prices over a certain number of periods and then dividing by the number of periods. It helps to identify the overall direction of the trend.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Places more weight on recent prices, making it more responsive to current market conditions. It is useful for identifying short-term trends.
Support and Resistance Levels in Market Cycle Understanding
Support and resistance levels are critical concepts in technical analysis that help traders understand market cycles. Support levels act as a floor for the price, where buying interest is strong enough to prevent the price from falling further. On the other hand, resistance levels act as a ceiling for the price, where selling pressure is significant enough to prevent the price from rising.
Support becomes resistance, and resistance becomes support when breached.
