Mutual funds vs. ETFs sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. If you’re ready to dive into the world of investment strategies, cost structures, liquidity, tax efficiency, diversification, and performance tracking, then buckle up and get ready for an informative ride.
Introduction
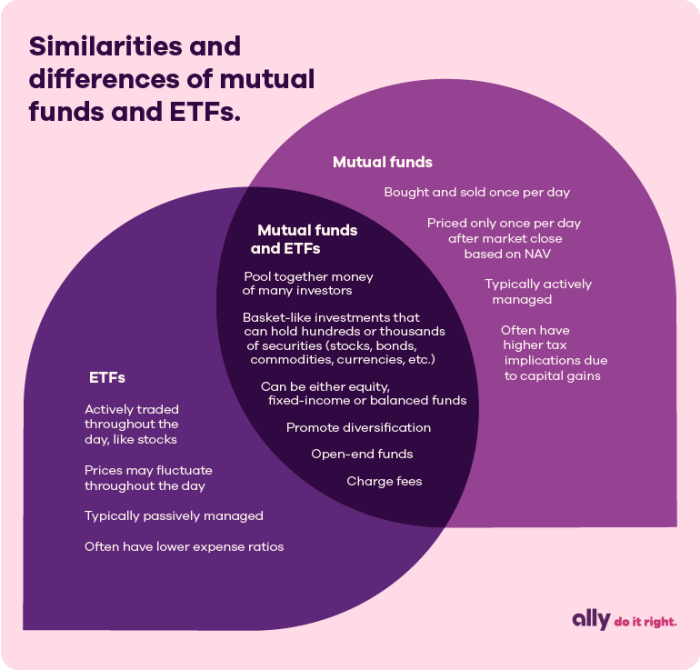
Mutual funds and ETFs are both investment vehicles that allow individuals to pool their money together to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. While they have similarities, there are key differences that set them apart.
Definition of Mutual Funds and ETFs
Mutual funds are professionally managed investment funds that pool money from multiple investors to purchase a diversified portfolio of securities. Investors in mutual funds buy shares of the fund itself, and the value of these shares fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying securities.
ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, are similar to mutual funds in that they also pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. However, ETFs are traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks, and their prices fluctuate throughout the trading day based on supply and demand.
How They Work
Mutual funds are priced once a day at the end of the trading day, based on the net asset value (NAV) of the underlying securities. Investors can buy or sell mutual fund shares at this price.
On the other hand, ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day at market prices. This allows investors to trade ETFs like individual stocks, with the ability to place limit orders, short sell, or buy on margin.
Key Differences
– Mutual funds are priced once a day at the end of the trading day, while ETFs can be traded throughout the day.
– Mutual funds are bought and sold directly through the fund company, while ETFs are traded on stock exchanges.
– Mutual funds may have minimum investment requirements, while ETFs can be purchased for the price of one share.
– Mutual funds may have sales charges or redemption fees, while ETFs typically have lower expense ratios.
Investment Strategy
When it comes to investment strategy, mutual funds and ETFs take different approaches to meet their financial goals.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are actively managed by professional fund managers who make decisions on where to allocate investors’ money. These funds typically aim to outperform a specific benchmark index or provide capital appreciation over the long term.
- Diversification: Mutual funds often spread their investments across a wide range of assets to reduce risk.
- Active Management: Fund managers actively buy and sell securities in an attempt to outperform the market.
- Long-term Focus: Mutual funds are usually geared towards long-term growth rather than short-term gains.
ETFs
On the other hand, ETFs are passively managed and aim to replicate the performance of a specific index or asset class. They are traded on the stock exchange like individual stocks.
- Index Tracking: ETFs typically track a specific index or sector, mirroring its performance.
- Low Cost: Due to passive management, ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
- Liquidity: ETFs can be bought and sold throughout the trading day at market prices.
Popular Investment Strategies
Examples of popular investment strategies for both mutual funds and ETFs include:
- Growth Investing: Focusing on companies with strong growth potential and high earnings.
- Value Investing: Seeking undervalued stocks with the potential for long-term growth.
- Income Investing: Prioritizing investments that generate regular income, such as dividends.
- Market Timing: Attempting to predict the market’s movements to buy low and sell high.
Cost Comparison
When comparing the cost structures of mutual funds and ETFs, it’s essential to consider various factors that can impact an investor’s bottom line. One of the key components to look at is the expense ratio, which represents the annual fee charged by the fund to cover operating expenses.
Expense Ratios
Expense ratios for mutual funds tend to be higher than those for ETFs. Mutual funds are actively managed, meaning there are higher costs associated with research and management decisions. On the other hand, ETFs are passively managed and typically have lower expense ratios since they aim to replicate the performance of a specific index rather than actively selecting investments.
- Mutual funds may have expense ratios ranging from 0.5% to 2%, while ETFs generally have expense ratios below 0.5%.
- Investors should be aware that even a seemingly small difference in expense ratios can significantly impact their returns over time.
Additional Fees
Apart from expense ratios, investors should also consider other fees that may come into play when investing in mutual funds or ETFs.
- Some mutual funds charge sales loads, which are fees paid either when buying (front-end load) or selling (back-end load) shares.
- ETFs typically do not have sales loads, making them a more cost-effective option for investors looking to avoid these additional charges.
- Both mutual funds and ETFs may incur trading costs, such as brokerage commissions, which investors should factor into their overall cost analysis.
Liquidity and Trading
When it comes to mutual funds and ETFs, understanding liquidity and trading is crucial for investors looking to make informed decisions about their investments.
Liquidity of Mutual Funds and ETFs
- Mutual funds are typically less liquid compared to ETFs since they are only priced and traded at the end of the trading day.
- ETFs, on the other hand, trade throughout the day on the stock exchange like individual stocks, providing investors with more flexibility in buying and selling.
Trading Process for Mutual Funds vs. ETFs
- When trading mutual funds, investors place orders directly with the fund company at the end of the trading day, and the price is based on the net asset value (NAV) calculated after market close.
- ETFs, however, are traded on the stock exchange through a brokerage firm at market prices, which may fluctuate throughout the day based on supply and demand.
Impact on Investor Decisions
- The liquidity and trading frequency of mutual funds and ETFs can impact investor decisions based on their investment goals and trading preferences.
- Investors seeking more flexibility and intraday trading opportunities may prefer ETFs due to their liquidity and ability to be traded throughout the day.
- On the other hand, investors looking for a long-term investment strategy with less focus on daily trading activity may opt for mutual funds despite their lower liquidity.
Tax Efficiency
When it comes to investing in mutual funds or ETFs, understanding the tax implications is crucial. Let’s dive into how tax efficiency plays a role in these investment options.
Tax Implications of Investing in Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds can have tax implications for investors. When mutual fund managers buy and sell securities within the fund, capital gains taxes are incurred. This means that investors may be subject to capital gains taxes even if they did not sell any shares themselves.
- Mutual funds distribute capital gains to shareholders annually, which are taxable.
- Investors may also face taxes on dividends and interest earned within the mutual fund.
- Capital gains taxes are triggered when the fund manager sells securities for a profit.
Tax Advantages of ETFs
Compared to mutual funds, ETFs offer tax advantages due to their unique structure. ETFs are bought and sold on exchanges like stocks, which can lead to lower capital gains taxes for investors.
- ETFs typically have lower portfolio turnover, resulting in fewer capital gains distributions.
- Investors have more control over when to realize capital gains when trading ETF shares.
- Creation and redemption process of ETFs can help minimize capital gains taxes.
Tax-Efficient Strategies for Investors
For investors considering mutual funds or ETFs, there are tax-efficient strategies that can be implemented to optimize returns and minimize tax liabilities.
- Consider investing in tax-efficient mutual funds that focus on minimizing capital gains distributions.
- Utilize tax-loss harvesting to offset capital gains with capital losses within your investment portfolio.
- Hold ETFs in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s to defer taxes on gains.
Diversification
When it comes to investing, diversification is key to managing risk and maximizing returns. Both mutual funds and ETFs offer investors the opportunity to diversify their portfolios across a wide range of assets, reducing the impact of any single investment on overall performance.
Mutual Funds Diversification
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. This pooling of resources allows individual investors to access a wide range of investments that they may not be able to afford on their own. Mutual funds are actively managed by professional fund managers who make decisions about which securities to buy and sell, with the goal of achieving the fund’s investment objectives.
ETFs Diversification
Similar to mutual funds, ETFs also offer diversification benefits by holding a basket of securities that track a specific index or sector. ETFs are traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks, but they provide investors with exposure to a diversified portfolio of assets. ETFs are typically passively managed, meaning they aim to replicate the performance of a specific index rather than actively selecting individual securities.
Comparison of Diversification
Both mutual funds and ETFs offer investors the opportunity to achieve diversification across a broad range of assets. However, the level of diversification achievable through mutual funds may vary depending on the fund’s investment strategy and holdings. ETFs, on the other hand, provide investors with diversification benefits similar to mutual funds but with the added flexibility of intraday trading on stock exchanges.
Performance Tracking
Tracking the performance of your investments is crucial to ensuring that you are on the right path towards your financial goals. For both mutual funds and ETFs, there are tools and methods available to help investors monitor their performance and make informed decisions.
Mutual Funds
- Mutual funds provide regular updates on their performance through their websites, investor reports, and financial news outlets.
- Investors can track the Net Asset Value (NAV) of the mutual fund to see how it has been performing over time.
- Comparing the mutual fund’s performance to its benchmark index can also give investors a better idea of how well it is doing.
ETFs
- ETFs are traded throughout the day on the stock exchange, so investors can monitor their real-time market price to track performance.
- Online brokerage accounts and financial websites provide up-to-date information on ETF prices and performance metrics.
- Investors can also compare the ETF’s performance to its underlying index or benchmark to evaluate how well it is tracking the market.
Comparison
When it comes to tracking and evaluating performance, ETFs have the advantage of real-time pricing and intraday trading, making it easier for investors to stay informed about their investments. On the other hand, mutual funds may provide more detailed reports and historical performance data, allowing investors to analyze long-term trends. Ultimately, the choice between mutual funds and ETFs for performance tracking will depend on your investment style and preferences.
