Kicking off with Understanding market cycles, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone american high school hip style that unfolds with each word.
Diving into the world of market cycles, we explore the different phases, factors influencing them, and strategies for navigating through these economic waves. Get ready to ride the rollercoaster of market trends!
Overview of Market Cycles
Market cycles in economics refer to the recurring patterns of expansion and contraction in economic activity over time. These cycles impact various aspects of the economy, including employment, production, and investment.
Types of Market Cycles
- Business Cycles: Business cycles are fluctuations in economic activity characterized by periods of expansion and contraction. These cycles typically consist of four phases: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough.
- Stock Market Cycles: Stock market cycles involve the rise and fall of stock prices over time. These cycles are influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, investor sentiment, and market speculation.
Significance of Understanding Market Cycles
- Investors: Understanding market cycles can help investors make informed decisions about when to buy or sell assets. By recognizing the stages of the cycle, investors can capitalize on opportunities for growth and mitigate risks during downturns.
- Economists: Economists study market cycles to analyze the overall health of the economy and predict future trends. By identifying patterns in market behavior, economists can provide insights into potential policy interventions and economic forecasts.
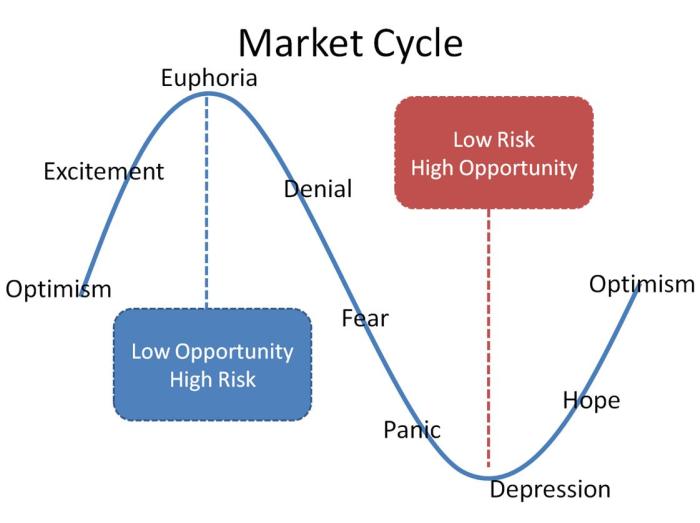
Phases of Market Cycles
In the world of finance and investing, market cycles play a crucial role in determining the overall health and performance of various asset classes. Understanding the typical phases of a market cycle is essential for investors to make informed decisions and navigate the ups and downs of the market.
The typical phases of a market cycle include expansion, peak, contraction, and trough. Each phase comes with its own set of characteristics and behaviors that can help investors anticipate market movements and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Expansion Phase
During the expansion phase, also known as the bull market, economic activity is on the rise, and asset prices are generally increasing. Investor confidence is high, leading to increased buying activity and overall positive market sentiment. This phase is characterized by strong GDP growth, low unemployment rates, and rising corporate profits.
- Stock prices are steadily increasing.
- Investor optimism is high, leading to more risk-taking.
- Interest rates are typically low, encouraging borrowing and spending.
Peak Phase
The peak phase marks the climax of the market cycle, where asset prices reach their highest levels before starting to decline. This phase is characterized by excessive optimism, overvaluation of assets, and a general sense of euphoria among investors. It is often a period of irrational exuberance and speculation.
- Asset prices hit all-time highs.
- Investor sentiment is at its peak, with a strong belief in continued growth.
- Risk of market correction or downturn starts to become more pronounced.
Contraction Phase
In the contraction phase, also known as the bear market, economic activity slows down, and asset prices begin to decline. Investor confidence wanes, leading to increased selling pressure and a general sense of pessimism in the market. This phase is characterized by falling GDP, rising unemployment, and declining corporate profits.
- Stock prices start to decline, often experiencing sharp drops.
- Investors become more risk-averse and start moving towards safer assets.
- Interest rates may start to rise as central banks try to stimulate the economy.
Trough Phase
The trough phase represents the lowest point of the market cycle, where asset prices have bottomed out, and investor sentiment is extremely negative. This phase is characterized by high levels of fear and uncertainty, as investors wait for signs of a market recovery.
- Asset prices are at their lowest levels.
- Investor sentiment is pessimistic, with a lack of confidence in the market.
- Opportunities for long-term investment may arise as valuations become attractive.
Factors Influencing Market Cycles
When it comes to understanding market cycles, it’s crucial to consider the various factors that can influence their direction and intensity. From economic indicators to geopolitical events and investor sentiment, a combination of factors can shape the cyclical nature of markets.
Economic Indicators Impacting Market Cycles
- Economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment levels play a significant role in influencing market cycles.
- Changes in interest rates by central banks can also impact market cycles by affecting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
- Consumer spending patterns and retail sales data can provide insights into the health of the economy and influence market cycles.
Geopolitical Events and Market Cycles
- Geopolitical events such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability can create uncertainty in the markets, leading to fluctuations in asset prices.
- Changes in government policies, regulations, or trade agreements can have a direct impact on market cycles by altering the business environment.
- Global events like natural disasters or pandemics can also disrupt market cycles by affecting supply chains and economic activity.
Investor Sentiment and Market Psychology
- Investor sentiment, or how investors feel about the market, can greatly influence market cycles as it drives buying and selling decisions.
- Market psychology, including fear, greed, and herd mentality, can create market bubbles or crashes, leading to exaggerated market cycles.
- The behavior of investors, influenced by emotions and cognitive biases, can amplify market movements and contribute to the cyclical nature of markets.
Strategies for Navigating Market Cycles
In the ever-changing landscape of the financial markets, having a solid strategy to navigate through market cycles is crucial for investors. Different phases of market cycles require different approaches to maximize returns and minimize risks. Let’s explore some effective strategies that investors can employ to capitalize on market cycles.
Different Investment Strategies for Each Phase of a Market Cycle
- During the expansion phase, it is advisable to focus on growth stocks and sectors that have the potential for high returns. This is the time to take on more risk in anticipation of continued market growth.
- As the market reaches its peak, investors should consider taking profits and rebalancing their portfolios to reduce exposure to overvalued assets. This is a good time to consider defensive stocks or sectors that are less affected by economic downturns.
- During the contraction phase, it may be wise to focus on income-generating investments such as dividend-paying stocks or bonds. This can provide a steady stream of income to offset potential losses in the market.
- When the market hits bottom, it presents opportunities for value investors to buy undervalued assets at discounted prices. This can lead to significant gains as the market eventually recovers.
Examples of Successful Strategies Used by Investors
- Legendary investor Warren Buffett is known for his value investing approach, which involves buying quality companies at reasonable prices and holding them for the long term.
- Hedge fund manager George Soros famously used a combination of fundamental analysis and market psychology to profit from market trends and cycles.
- Some investors opt for a passive index fund strategy, which involves investing in a diversified portfolio that tracks a broad market index. This approach can help mitigate risk and ensure consistent returns over time.
Importance of Diversification and Risk Management
Diversification is key to navigating through market cycles successfully. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their overall portfolio. Additionally, effective risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and maintaining a cash reserve, can help protect against significant losses during market downturns.
