Get ready to dive into the world of financial statements like never before! This guide will take you on a journey through the intricate details of business numbers, offering you a unique perspective that will sharpen your financial acumen in no time.
From understanding the purpose of financial statements to analyzing crucial ratios, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in the business world.
Understanding Financial Statements
Financial statements play a crucial role in providing a snapshot of a company’s financial health and performance. They are essential tools used by investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to assess the financial position of a business.
Purpose of Financial Statements
- Income Statement: Shows the company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period, resulting in the net income or loss.
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Cash Flow Statement: Details the flow of cash in and out of the business, showing how cash is generated and used.
Importance of Reading Financial Statements
Financial statements help stakeholders make informed decisions about investing, lending, or working with a company. By accurately interpreting financial statements, individuals can assess a company’s profitability, liquidity, and overall financial health, guiding their actions and strategies.
Components of Financial Statements
Financial statements are crucial tools that provide insight into a company’s financial health. Understanding the key components of these statements is essential for making informed decisions as an investor or stakeholder.
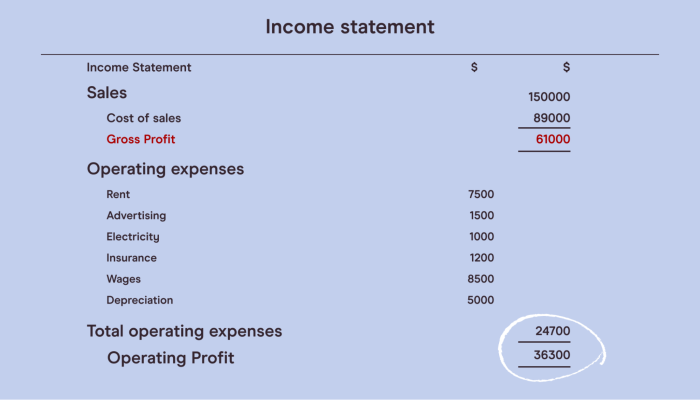
Income Statement Components
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, provides a summary of a company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period. The key components of an income statement include:
- Revenue: the total amount of money earned from sales of goods or services.
- Expenses: the costs incurred in the process of generating revenue, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Net Income: the difference between total revenue and total expenses, representing the company’s profit or loss.
Balance Sheet Elements
A balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It consists of three main elements:
- Assets: resources owned by the company, such as cash, inventory, and property.
- Liabilities: obligations or debts owed by the company, including loans and accounts payable.
- Equity: the difference between total assets and total liabilities, representing the owner’s stake in the company.
Cash Flow Statement Information
The cash flow statement shows how changes in balance sheet accounts and income affect cash and cash equivalents. It includes the following information:
- Cash from Operating Activities: cash generated from the company’s core business operations.
- Cash from Investing Activities: cash flow from the buying and selling of long-term assets.
- Cash from Financing Activities: cash flow related to external financing, such as issuing debt or repurchasing shares.
Analyzing Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are key tools used to evaluate a company’s financial health and performance. By analyzing these ratios, investors and analysts can gain insight into various aspects of a company’s operations, profitability, liquidity, and solvency.
Common Financial Ratios
- Profitability Ratios: These ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profits relative to its revenue, assets, or equity. Examples include:
- Return on Equity (ROE) = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
- Profit Margin = Net Income / Revenue
- Liquidity Ratios: These ratios assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Examples include:
- Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
- Quick Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventory) / Current Liabilities
- Solvency Ratios: These ratios evaluate a company’s long-term financial stability and ability to meet its long-term debt obligations. Examples include:
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Debt / Shareholders’ Equity
- Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense
Reading Notes to the Financial Statements
Understanding the notes to the financial statements is crucial as they provide additional details and explanations that are not included in the main financial statements.
Purpose of Notes to the Financial Statements
- Explain accounting policies and methods used
- Provide additional details on specific accounts
- Disclose contingent liabilities and commitments
- Give explanations for significant transactions
Types of Information Typically Disclosed in the Notes
- Details on revenue recognition policies
- Inventory valuation methods
- Details on property, plant, and equipment
- Employee benefit plans
Insights from Notes on Financial Performance
- Helps in understanding the basis of financial statement preparation
- Provides clarity on unusual items or transactions
- Discloses potential risks and uncertainties
- Details on related party transactions
Using Financial Statements for Decision Making
Financial statements play a crucial role in decision making, especially when it comes to investments, comparing companies, and strategic planning. Let’s dive into how these statements can be utilized effectively.
Making Investment Decisions
- Investors can use financial statements to analyze a company’s profitability, liquidity, and overall financial health before making investment decisions.
- By examining key ratios such as return on investment (ROI) and earnings per share (EPS), investors can assess the potential returns and risks associated with investing in a particular company.
- Comparing financial statements of different companies in the same industry can help investors identify the strongest investment opportunities and make informed decisions.
Comparing Financial Statements of Different Companies
- When comparing financial statements of different companies, it is essential to focus on key performance indicators such as revenue growth, profit margins, and debt levels.
- Investors should also consider factors like industry trends, market conditions, and competitive positioning to make a comprehensive analysis.
- Ratio analysis, including liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and leverage ratios, can provide valuable insights into how companies stack up against each other.
Role in Strategic Planning and Forecasting
- Financial statements serve as a roadmap for strategic planning by helping companies set realistic goals, allocate resources effectively, and measure performance over time.
- Forecasting future financial performance based on historical data and trends from financial statements can assist in making strategic decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- By utilizing financial statements in strategic planning, companies can optimize their operations, identify growth opportunities, and mitigate potential risks in a proactive manner.
