Financial regulations in the U.S. sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Get ready to dive deep into the intricate world of financial regulations in the U.S., where rules and oversight shape the financial landscape in ways you never imagined.
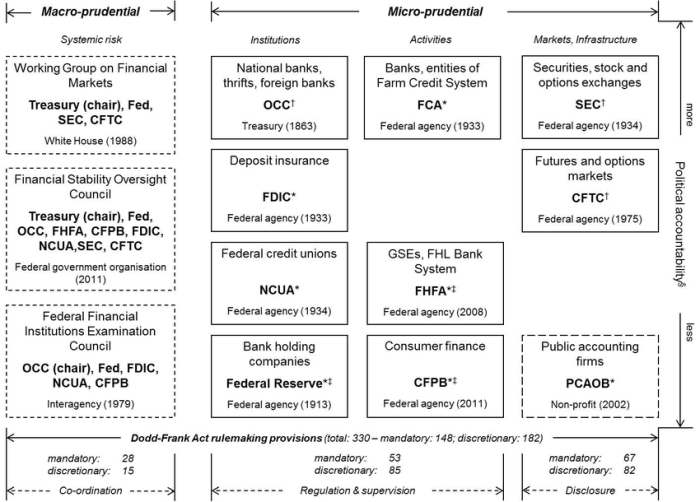
Overview of Financial Regulations in the U.S.
Financial regulations in the U.S. are put in place to ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system, protect consumers, and prevent activities that could lead to another financial crisis like the one in 2008.
Key Regulatory Bodies
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): Responsible for regulating securities markets and protecting investors.
- The Federal Reserve: Oversees monetary policy and regulates banks to ensure financial stability.
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB): Focuses on protecting consumers in the financial sector from abusive practices.
Impact on the Economy
Financial regulations play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy economy by preventing fraud, ensuring fair competition, and promoting transparency in financial transactions. They help build trust in the financial system, which is essential for businesses and individuals to invest and grow. By monitoring and enforcing these regulations, the government aims to minimize risks and maintain the overall stability of the economy.
History of Financial Regulations in the U.S.
The history of financial regulations in the U.S. dates back to the early 20th century, marked by significant events that led to the establishment of a framework to oversee and regulate the financial sector.
Timeline of Significant Events
- 1907: Panic of 1907 – A financial crisis that highlighted the need for regulatory measures to stabilize the financial system.
- 1913: Federal Reserve Act – Established the Federal Reserve System to supervise banks and implement monetary policy.
- 1929: Stock Market Crash – Led to the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 to regulate securities markets.
- 1933: Glass-Steagall Act – Erected barriers between commercial and investment banking to prevent conflicts of interest.
Evolution of Financial Regulations
The evolution of financial regulations in the U.S. has been shaped by changing economic landscapes and the emergence of new financial instruments. Over the years, regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have been established to oversee different aspects of the financial markets.
Key Legislative Acts
- The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 – Implemented in response to the 2008 financial crisis, aimed at enhancing financial stability and consumer protection.
- The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act of 1999 – Repealed parts of the Glass-Steagall Act, allowing for the combination of commercial and investment banking activities.
- The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 – Enacted to improve corporate governance and accountability in the wake of accounting scandals such as Enron and WorldCom.
Types of Financial Regulations
In the realm of financial regulations in the U.S., there are two main categories that play a crucial role in maintaining stability and protecting consumers: prudential regulations and conduct regulations.
Prudential Regulations vs. Conduct Regulations
Prudential regulations focus on the financial health and stability of institutions, such as banks and insurance companies. These regulations set standards for capital requirements, liquidity ratios, and risk management practices to ensure that financial institutions can withstand financial shocks and crises.
Conduct regulations, on the other hand, are geared towards promoting fair and ethical behavior within the financial sector. These regulations govern how financial institutions interact with their clients, ensuring transparency, honesty, and accountability in their dealings.
Role of Capital Requirements
Capital requirements are a key component of prudential regulations that mandate financial institutions to maintain a certain level of capital to cover potential losses. By requiring banks and other institutions to hold adequate capital reserves, regulators aim to enhance the stability and resilience of the financial system. Adequate capital cushions can help prevent insolvency and reduce the likelihood of a financial institution’s failure, protecting depositors and investors.
Importance of Consumer Protection Regulations
Consumer protection regulations are designed to safeguard the interests of individuals and businesses that engage with financial institutions. These regulations cover a wide range of areas, including disclosure requirements, fair lending practices, and prohibitions on deceptive financial products. By enforcing these regulations, regulators aim to prevent fraud, abuse, and exploitation of consumers in the financial sector, promoting trust and confidence in the system.
Enforcement of Financial Regulations
Ensuring compliance with financial regulations is crucial to maintaining stability and integrity in the financial system.
Enforcement Mechanisms
Regulatory authorities employ various enforcement mechanisms to uphold financial regulations, such as:
- Regular audits and inspections to monitor compliance
- Issuance of fines and penalties for violations
- Suspension or revocation of licenses for non-compliance
- Legal actions and prosecution against offenders
Penalties Imposed
Financial institutions face significant penalties for regulatory violations, including:
- Monetary fines ranging from thousands to millions of dollars
- Loss of reputation and customer trust
- Potential criminal charges for severe violations
Challenges Faced by Regulatory Authorities
Enforcing financial regulations effectively poses several challenges for regulatory authorities, such as:
- Complexity of financial products and transactions
- Rapidly evolving technology and digital platforms
- Limited resources and staffing for oversight
- Globalization and cross-border regulatory issues
