Diving deep into the world of asset allocation strategies, this introduction sets the stage for an exciting exploration of how to effectively manage your investments like a boss. From traditional approaches to cutting-edge techniques, get ready to level up your financial game with some serious knowledge drops.
Introduction to Asset Allocation Strategies
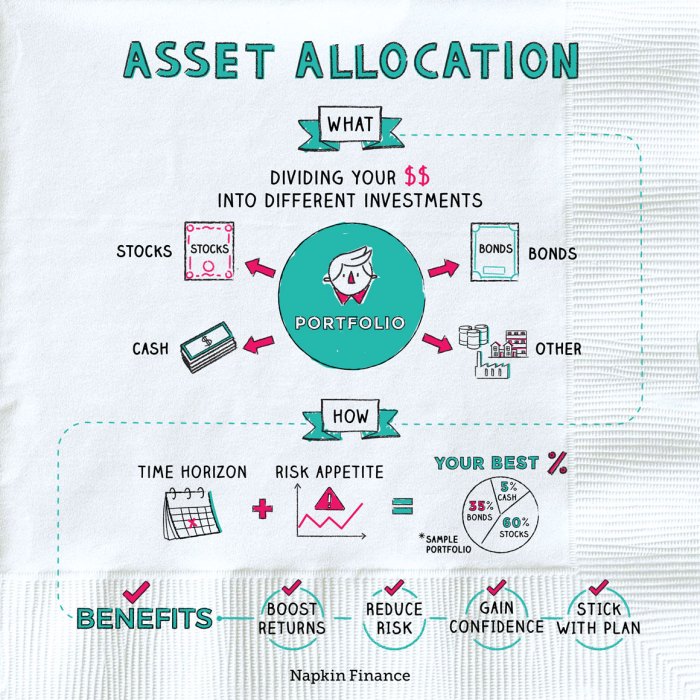
Asset allocation strategies refer to the process of dividing an investment portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. This strategic distribution helps investors achieve their financial goals while managing risk effectively.
Asset allocation is crucial in investment portfolios as it can significantly impact returns and risk levels. By diversifying across various asset classes, investors can reduce the overall risk of their portfolio and potentially enhance returns over the long term.
Examples of Different Asset Classes
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for high returns but come with higher volatility.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing fixed income with lower risk compared to stocks.
- Cash Equivalents: Short-term, low-risk investments such as Treasury bills or money market funds offering liquidity and stability.
Role of Risk Tolerance in Asset Allocation
Risk tolerance plays a crucial role in determining asset allocation strategies as it reflects an investor’s ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to stocks, seeking higher returns despite the increased volatility. On the other hand, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative allocation with a higher proportion of bonds and cash equivalents.
Traditional Asset Allocation Strategies
Strategic asset allocation involves setting a target mix of asset classes and sticking to it through various market conditions. This approach typically involves a long-term view and focuses on the investor’s risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon.
Pros and Cons of Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation offers several advantages, such as diversification, risk management, and the potential for long-term growth. By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their portfolios.
However, one of the drawbacks of strategic asset allocation is that it may not always respond quickly to changing market conditions. This static approach could result in missed opportunities or losses during periods of rapid market fluctuations.
Examples of Asset Allocation Models
One of the most well-known asset allocation models is the Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT), developed by Harry Markowitz. MPT emphasizes the importance of diversification and the relationship between risk and return in building an optimal portfolio.
Comparison with Other Approaches
When comparing traditional asset allocation strategies with other approaches like tactical asset allocation or dynamic asset allocation, the key difference lies in the level of flexibility and responsiveness to market changes. While traditional strategies take a more passive and long-term view, other approaches may involve more active management and adjustments based on market conditions.
Tactical Asset Allocation Strategies
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to a portfolio’s asset allocation based on current market conditions. Unlike strategic asset allocation, which is more of a long-term approach, tactical asset allocation is dynamic and responsive to changing market trends.
Advantages of Tactical Asset Allocation
- Flexibility: Tactical asset allocation allows investors to quickly adapt to market changes and take advantage of short-term opportunities.
- Potential for higher returns: By actively adjusting the allocation based on market conditions, there is potential to outperform the market over the short term.
- Risk management: Tactical asset allocation can help mitigate risks by reducing exposure to underperforming assets during downturns.
Disadvantages of Tactical Asset Allocation
- Higher costs: The frequent trading and monitoring required for tactical asset allocation can lead to higher transaction costs and fees.
- Market timing risks: Making incorrect predictions about market movements can result in missed opportunities or losses.
- Overtrading: Constantly adjusting the portfolio can lead to overtrading, which may erode returns due to transaction costs.
Examples of Tactical Asset Allocation Techniques
- Market timing: This involves making allocation decisions based on short-term market trends, economic indicators, or technical analysis.
- Sector rotation: Rotating investments among different sectors based on their performance outlook and economic conditions.
- Risk parity: Allocating assets based on risk levels rather than traditional market capitalization weights.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Tactical Asset Allocation Decisions
Economic conditions such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth can significantly influence tactical asset allocation decisions. For example, during periods of high inflation, investors may shift towards commodities or real assets to hedge against purchasing power erosion. Similarly, in a low-interest-rate environment, investors may favor equities over fixed income for higher potential returns.
Alternative Asset Allocation Strategies
When it comes to diversifying your investment portfolio, alternative asset allocation strategies like dynamic asset allocation can play a crucial role in managing risk and maximizing returns.
Benefits of Diversification Through Alternative Assets
Alternative assets such as real estate, commodities, and cryptocurrencies offer unique benefits that traditional asset classes may not provide. By including these alternative assets in your portfolio, you can reduce overall volatility and enhance potential returns.
Examples of Alternative Asset Classes
- Real Estate: Investing in properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs) can offer a hedge against inflation and provide steady income through rental payments.
- Commodities: Assets like gold, silver, or oil can serve as a store of value and provide diversification benefits, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum offer the potential for high returns but also come with higher volatility compared to traditional investments.
Risk-Return Profiles of Traditional vs. Alternative Asset Allocation Strategies
Traditional asset allocation strategies typically focus on a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to achieve a balance of risk and return. On the other hand, alternative asset allocation strategies introduce a wider range of assets that may have different risk-return profiles. While traditional strategies offer stability and consistent returns, alternative strategies can offer higher potential returns but also come with increased volatility and risk.
