Get ready to dive into the world of Best budgeting methods where financial stability meets smart strategies, creating a recipe for success. This guide is your ticket to mastering the art of budgeting with style and flair.
In this guide, we will explore various budgeting methods, from traditional approaches to modern techniques, giving you the tools you need to take control of your finances.
Overview of Budgeting Methods
Budgeting methods refer to the various strategies and techniques individuals or organizations use to manage their finances effectively. These methods help in planning, tracking, and controlling expenses to achieve financial goals and stability.
Using budgeting methods is crucial for financial stability as they provide a clear roadmap for managing income and expenses. By creating a budget, individuals can prioritize spending, avoid debts, and save for future needs. It also helps in identifying unnecessary expenses and making informed financial decisions.
Implementing effective budgeting strategies comes with numerous benefits. It allows individuals to track their financial progress, set realistic financial goals, and adjust spending habits accordingly. Budgeting methods also help in building an emergency fund, reducing financial stress, and improving overall financial well-being.
Traditional Budgeting Methods
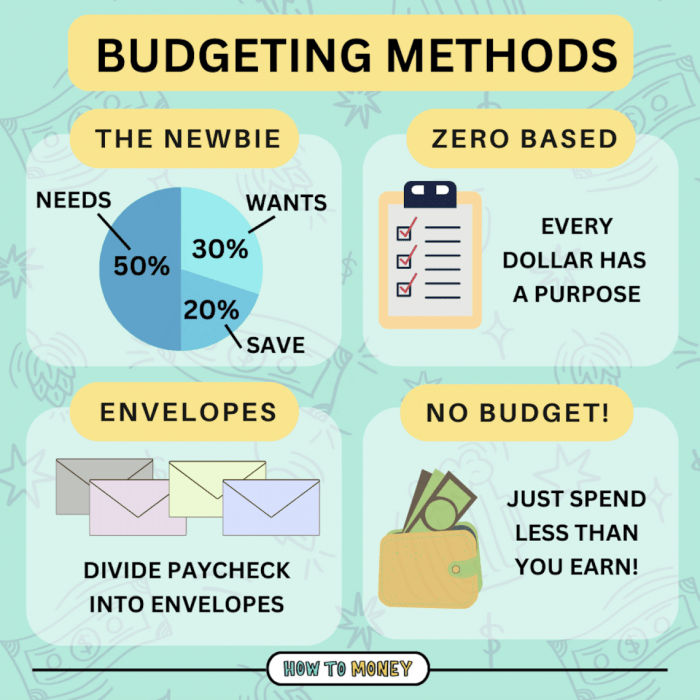
Traditional budgeting methods refer to the conventional ways of creating and managing budgets that have been used for many years. These methods typically involve forecasting expenses and revenues based on historical data and making decisions accordingly.
Comparison with Modern Approaches
Traditional budgeting methods are often criticized for being rigid and time-consuming compared to modern approaches such as zero-based budgeting or activity-based budgeting. While traditional methods rely heavily on past performance to predict future outcomes, modern approaches focus more on aligning budgets with organizational goals and objectives.
- Incremental Budgeting: This is a common traditional budgeting technique where budgets are prepared by adjusting the previous year’s budget by a certain percentage. While this method is simple and easy to implement, it may lead to budgetary slack and inefficiencies.
- Fixed Budgeting: In fixed budgeting, a budget is set at the beginning of the period and remains unchanged regardless of actual performance. This method can be inflexible and may not account for changes in the business environment.
- Historical Budgeting: Historical budgeting involves using past financial data to estimate future expenses and revenues. While this method is straightforward, it may not be suitable for rapidly changing industries or unpredictable market conditions.
Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting is a method where all expenses must be justified for each new budget period, as opposed to simply adjusting the previous period’s budget. This approach forces companies to start from scratch and allocate funds based on needs and costs, rather than just making incremental changes.
Definition and Difference from Traditional Methods
Zero-Based Budgeting differs from traditional budgeting methods in that it requires all expenses to be justified from zero, rather than basing the new budget on the previous period’s budget. This means that each expense must be evaluated and approved based on its necessity and cost-effectiveness, leading to a more efficient allocation of resources.
Creating a Zero-Based Budget
To create a zero-based budget, companies must first identify their needs and costs for the upcoming period. This involves analyzing each expense and determining whether it is essential for the operations of the business. Once all expenses have been justified, the budget is then created based on these needs and costs, ensuring that every dollar is allocated wisely.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zero-Based Budgeting
- Advantages:
- Forces companies to reevaluate their expenses and eliminate unnecessary costs.
- Promotes cost efficiency and resource allocation based on actual needs.
- Encourages better decision-making and prioritization of expenses.
- Disadvantages:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive to implement.
- May lead to short-term budget cuts that can impact long-term goals.
- Requires detailed tracking and monitoring of expenses to ensure accuracy.
Envelope System
The envelope system is a budgeting method where you allocate a certain amount of cash to different categories of expenses and keep that cash in separate envelopes.
The envelope system works by dividing your income into categories such as groceries, entertainment, gas, and more. You then put the designated amount of cash for each category into its respective envelope. This helps you visually see how much money you have left for each expense and prevents overspending.
Tips for Implementing the Envelope System Effectively
- Label your envelopes clearly to avoid confusion.
- Regularly review your spending to ensure you are staying within your budget.
- Consider using digital envelopes or apps if carrying cash is not convenient for you.
- Adjust your budget categories as needed based on changes in your expenses.
50/30/20 Budgeting Rule
The 50/30/20 budgeting rule is a popular method of allocating your income where you divide it into three categories: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings and debt repayment. This rule provides a simple and structured way to manage your finances effectively.
Explanation of the 50/30/20 Budgeting Rule
- 50% for needs: This category includes essential expenses such as rent, utilities, groceries, transportation, and healthcare.
- 30% for wants: This portion is for discretionary spending like dining out, entertainment, shopping, and other non-essential items.
- 20% for savings and debt repayment: This part of your income should be allocated towards savings, investments, emergency fund, and paying off any outstanding debts.
Examples of Allocating Income
- For a monthly income of $3000:
- $1500 (50%) for needs
- $900 (30%) for wants
- $600 (20%) for savings and debt repayment
- For a monthly income of $5000:
- $2500 (50%) for needs
- $1500 (30%) for wants
- $1000 (20%) for savings and debt repayment
Flexibility and Limitations
The 50/30/20 budgeting approach provides a clear guideline for managing your finances, ensuring you prioritize essential needs, indulge in wants, and save for the future. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with high living costs or significant debt obligations.
Pay Yourself First Method
The Pay Yourself First method is a budgeting strategy that involves prioritizing saving money before allocating funds to other expenses. This approach emphasizes the importance of setting aside a portion of your income for savings first, rather than saving whatever is left after expenses.
Concept of the Pay Yourself First Method
The concept of the Pay Yourself First method is simple – you treat your savings like a non-negotiable expense that must be paid before anything else. By prioritizing saving money, you ensure that you are building your financial future and working towards your long-term goals.
Steps to Prioritize Saving
- 1. Determine a specific percentage of your income to save each month, such as 10% or 20%.
- 2. Set up an automatic transfer to move this percentage into a separate savings account as soon as you receive your paycheck.
- 3. Only budget and spend the money that is left after you have saved your predetermined percentage.
- 4. Adjust your budget and expenses accordingly if needed to ensure you consistently save the set percentage.
Impact on Long-Term Financial Goals
The Pay Yourself First method can have a significant impact on your long-term financial goals. By consistently saving a portion of your income first, you are building a strong financial foundation and working towards achieving milestones such as retirement savings, buying a home, or investing for the future. This method helps you prioritize your financial security and future needs over immediate wants, leading to better financial habits and overall stability.
