Yo, listen up! Student loan repayment options are where it’s at. Get ready to dive into the world of paying back those loans with style and smarts. Let’s break it down and make sure you’re in the know.
Now, let’s get down to the nitty-gritty details about different repayment plans and how they can work for you.
Overview of Student Loan Repayment Options
Student loan repayment options refer to the various plans available to borrowers for paying back their student loans after completing their education. It is essential for borrowers to understand these options to effectively manage their debt and avoid default.
Common Types of Student Loan Repayment Plans
There are several common types of student loan repayment plans designed to meet the diverse needs of borrowers:
- Standard Repayment Plan: This plan involves fixed monthly payments over a period of 10 years.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: Payments start low and increase every two years over a period of 10 years.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans set monthly payments based on the borrower’s income, family size, and loan amount.
- Extended Repayment Plan: This plan extends the repayment period beyond the standard 10 years.
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): This program forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans after 120 qualifying payments for borrowers working in public service.
Importance of Understanding Repayment Options
Understanding student loan repayment options is crucial for borrowers to choose the plan that best fits their financial situation. It allows borrowers to make informed decisions, avoid default, and effectively manage their debt burden without facing financial hardship.
Standard Repayment Plan
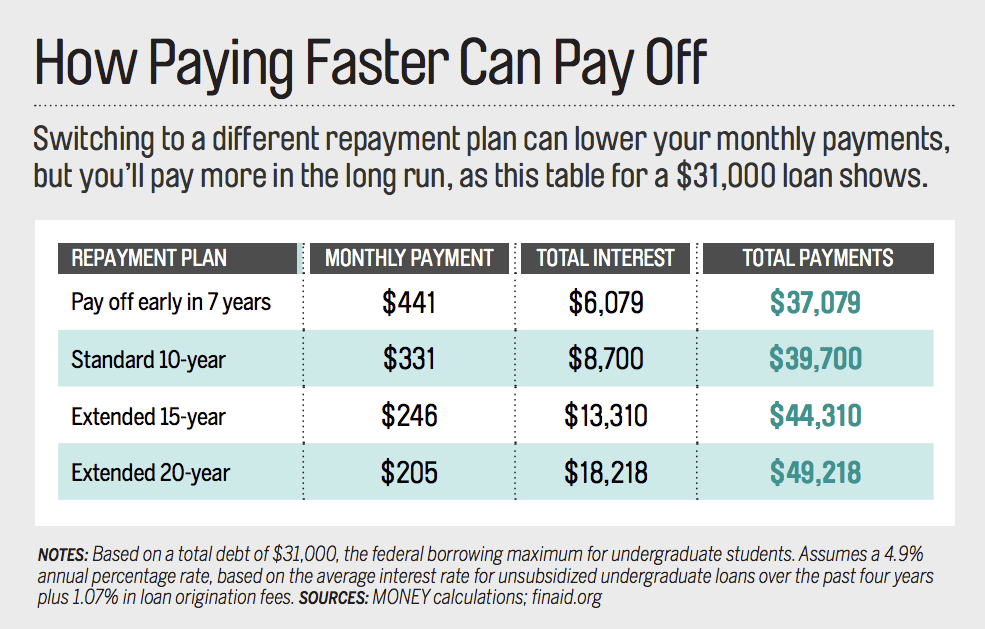
The Standard Repayment Plan is a popular option for borrowers looking to pay off their student loans in a fixed amount each month over a period of 10 years. This plan offers a predictable payment schedule and typically results in the lowest total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Features of the Standard Repayment Plan
- Fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period
- Lowest total interest paid compared to other repayment plans
- No income requirements
Who may benefit most from this plan
- Borrowers with stable incomes who can afford fixed monthly payments
- Individuals who want to pay off their loans quickly and minimize interest costs
Examples of how the Standard Repayment Plan works
- John has $30,000 in student loans with a 5% interest rate. Under the Standard Repayment Plan, he will make fixed monthly payments of approximately $318 for 10 years, totaling $38,160 including interest.
- Emily has $50,000 in student loans with a 6% interest rate. With the Standard Repayment Plan, she will make fixed monthly payments of around $555 for a decade, paying a total of $66,600 including interest.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-Driven Repayment Plans are options for repaying federal student loans based on a borrower’s income, family size, and other factors. These plans are designed to make monthly payments more manageable for borrowers who may have lower income levels.
Types of Income-Driven Plans
- Income-Based Repayment (IBR): This plan caps monthly payments at 10-15% of discretionary income, depending on when the borrower first took out loans.
- Pay As You Earn (PAYE): Monthly payments are also capped at 10% of discretionary income, but eligibility is limited to newer borrowers.
- Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE): This plan sets monthly payments at 10% of discretionary income for most borrowers, regardless of when loans were taken out.
Eligibility Criteria
- Borrowers with federal student loans are generally eligible for income-driven repayment plans.
- Each plan has specific criteria regarding when the loans were disbursed, the type of loans, and the borrower’s income level.
- Applicants must submit documentation of income and family size to determine eligibility and calculate monthly payments.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
In addition to repayment plans, there are also options for loan forgiveness programs designed to help individuals alleviate the burden of their student loans. These programs offer a way to have a portion or the entirety of the debt forgiven under certain circumstances.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) is a program that forgives the remaining balance on federal Direct Loans after making 120 qualifying payments while working full-time for a qualifying employer. Qualifying employers include government organizations, non-profit organizations, and other public service organizations.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness
Teacher Loan Forgiveness is a program that forgives up to $17,500 in federal student loans for teachers who work full-time for five complete and consecutive years in a low-income school or educational service agency.
Income-Driven Repayment Plan Forgiveness
Under certain income-driven repayment plans, any remaining loan balance can be forgiven after making payments for 20-25 years, depending on the plan. This forgiveness is considered taxable income.
Perkins Loan Cancellation
For individuals working in certain professions such as teaching, nursing, law enforcement, or the military, there may be opportunities to have a percentage of their Perkins Loans canceled for each year of service.
Healthcare Professionals Loan Forgiveness
Healthcare professionals in fields such as nursing, medicine, and dentistry may be eligible for loan forgiveness programs that require working in underserved areas or healthcare facilities with a shortage of medical professionals.
State-Specific Loan Forgiveness Programs
Many states offer their own loan forgiveness programs for residents working in specific professions or areas designated as high-need. These programs vary by state and may cover a portion or the entirety of the student loan debt.
Loan Consolidation
When it comes to student loans, consolidation is a process where multiple loans are combined into one new loan. This can make repayment more manageable by simplifying the process and potentially reducing monthly payments.
How Loan Consolidation Works
Loan consolidation involves taking out a new loan to pay off existing student loans. This new loan typically has a fixed interest rate based on the average of the interest rates of the loans being consolidated. Once the new loan is used to pay off the old loans, borrowers will make a single monthly payment towards the consolidated loan.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Loan Consolidation
- Benefits:
- Streamlined Repayment: Consolidating loans simplifies repayment by combining multiple loans into one.
- Potential for Lower Monthly Payments: Consolidation can potentially lower monthly payments by extending the repayment term.
- Drawbacks:
- Longer Repayment Term: Extending the repayment term through consolidation can result in paying more interest over time.
- Loss of Benefits: Consolidating federal loans into a private loan may result in losing borrower benefits such as loan forgiveness or income-driven repayment plans.
Step-by-Step Guidance on Loan Consolidation
- Evaluate Your Loans: Determine which loans are eligible for consolidation and calculate the total amount to be consolidated.
- Choose a Lender: Decide whether to consolidate through a federal Direct Consolidation Loan or a private lender.
- Apply for Consolidation: Complete the application process, providing necessary information and documents.
- Review Terms: Understand the terms of the new consolidated loan, including interest rate, repayment term, and monthly payment amount.
- Start Repayment: Begin making payments on the new consolidated loan according to the agreed-upon terms.
Refinancing Student Loans
When it comes to refinancing student loans, it’s all about getting a new loan to pay off existing student loans. This can help you secure a lower interest rate, reduce your monthly payments, or change your repayment terms to better suit your financial situation.
When to Consider Refinancing
- If you have a good credit score and steady income, refinancing can help you qualify for a lower interest rate, potentially saving you money in the long run.
- Refinancing can be a good option if you have multiple loans with varying interest rates and want to streamline your payments into one.
- When you want to switch from a variable interest rate to a fixed interest rate, refinancing can provide stability in your monthly payments.
How to Refinance Student Loans and Potential Risks
- Shop around for lenders and compare offers to find the best deal for your situation.
- Submit an application with the chosen lender, providing all necessary documentation for review.
- If approved, the new lender will pay off your existing loans, and you’ll start making payments on the new loan according to the agreed-upon terms.
- Potential risks include losing federal loan benefits like income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs, as well as extending the repayment period and paying more interest over time.
